Substitution Effect Definition And Example

A product may lose market share for many.
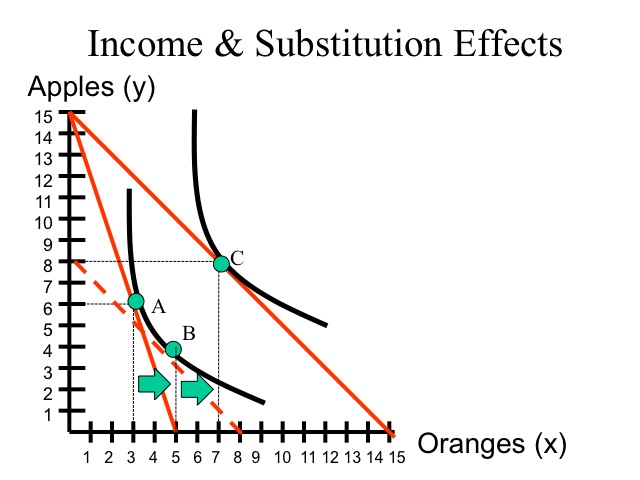
Substitution effect definition and example. It is the result of price increases if the consumer s budget stays the same. The substitution effect is harmful to economic prosperity overall because it limits the breadth of options and opportunities available to both consumers and producers. Thus every week you drink two bottles of orange juice and one bottle of apple juice. John eats rice that costs 5 per pound and pasta that costs 10 per.
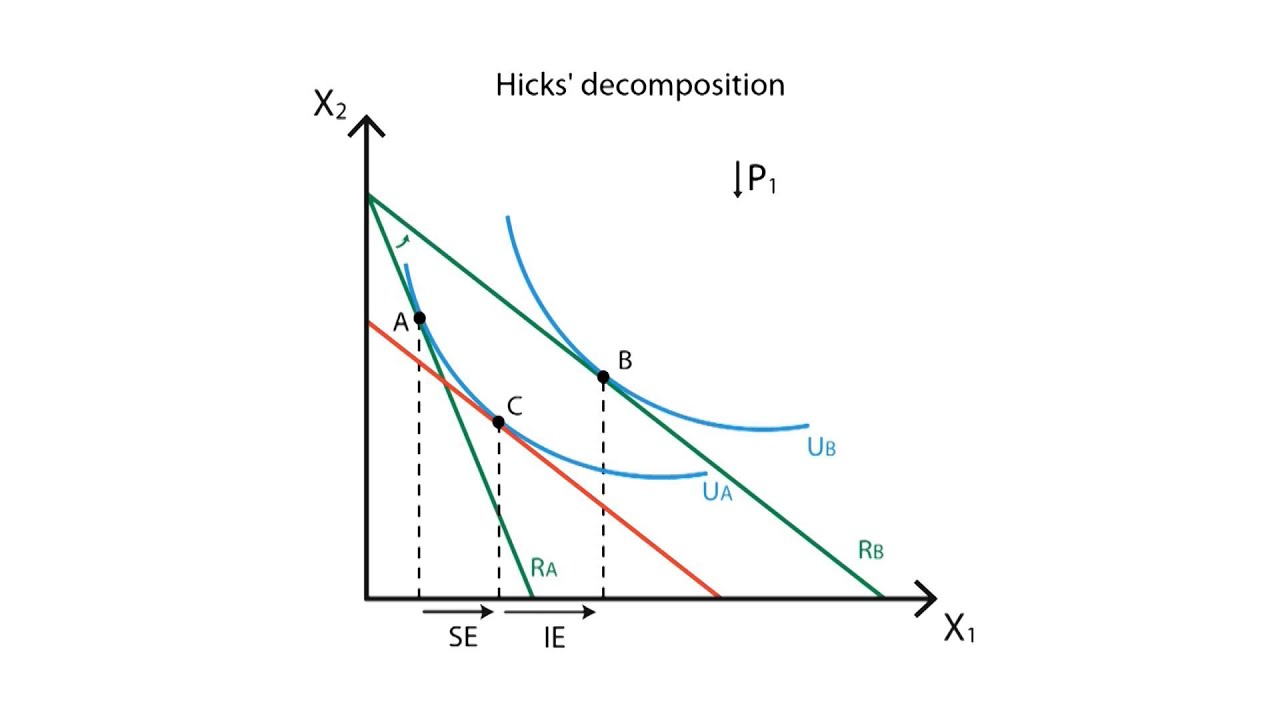
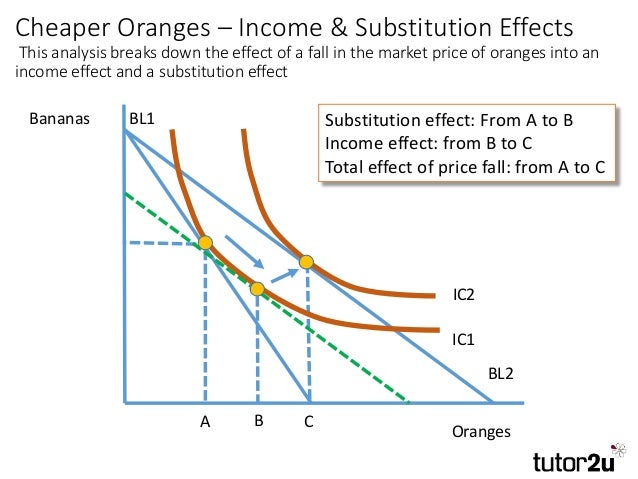
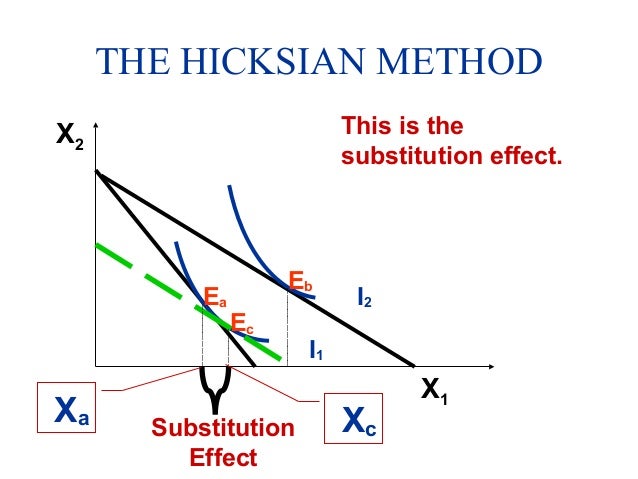
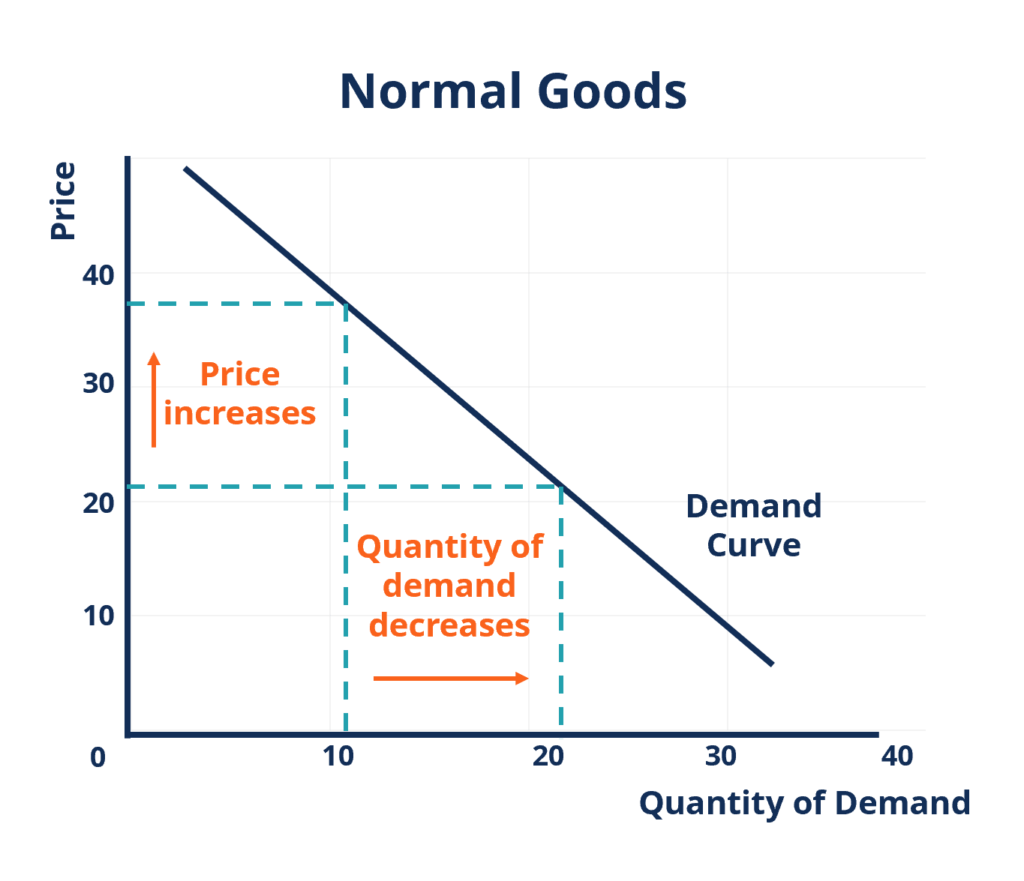
For example when the price of a good rises it becomes more expensive relative to other goods in the market. The substitution effect is an economic consequence of a rise in prices where customers are forced to replace a good they currently buy for a cheaper one. Let s say you buy apple juice at 5 per 16 ounce bottle and orange juice at 2 50 per 16 ounce bottle. A very common example of the substitution effect at work is when the price of chicken or red meat rises suddenly.
The substitution effect is the decrease in sales for a product that can be attributed to consumers switching to cheaper alternatives when its price rises. Consider the following example. One bottle of apple juice is equal in cost to two bottles of orange juice. For instance when the price of steak and other red meat increases over the.
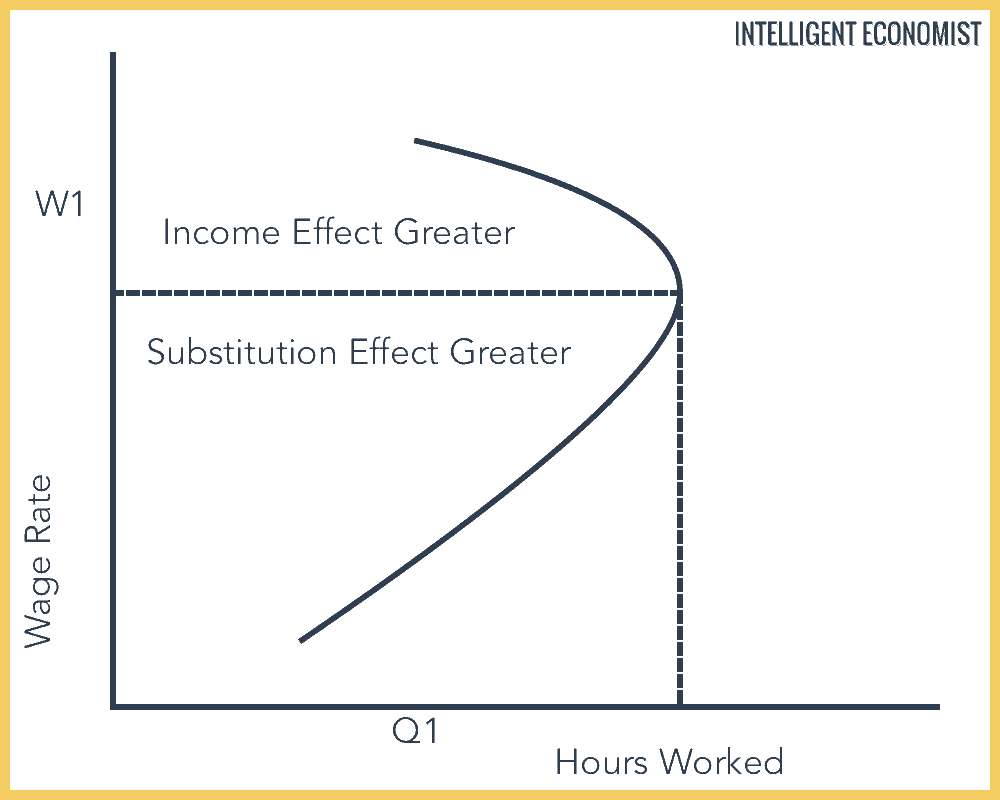
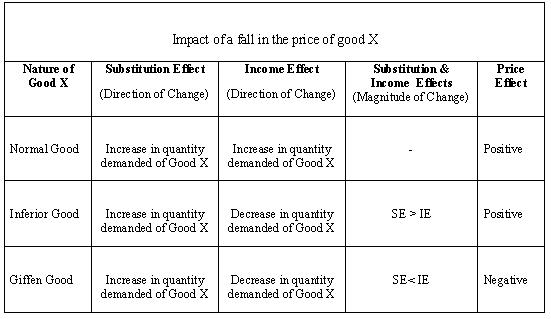
The substitution effect refers to the change in demand for a good as a result of a change in the relative price of the good compared to that of other substitute goods.