Income Consumption Curve According To Indifference Curve Theory

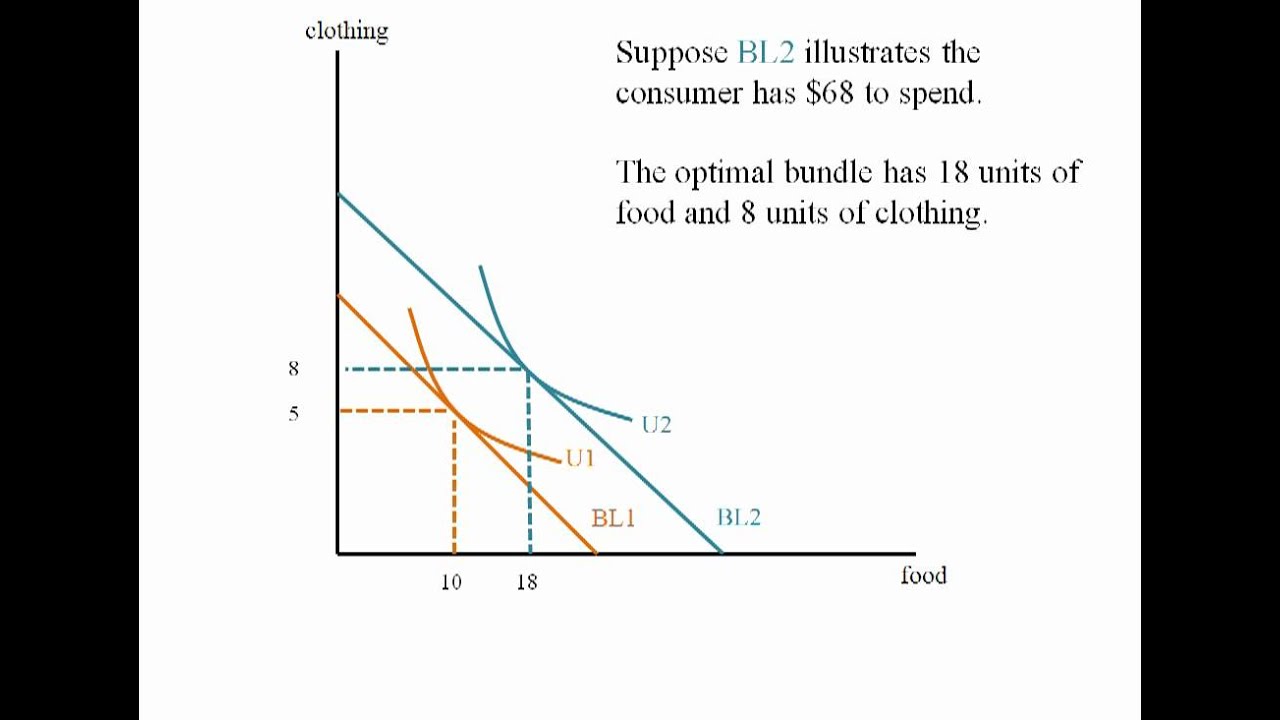
The optimal consumption combination is e 1 on indifference curve u 1 at which the consumer buys same ox units of good x as it is a neutral good.
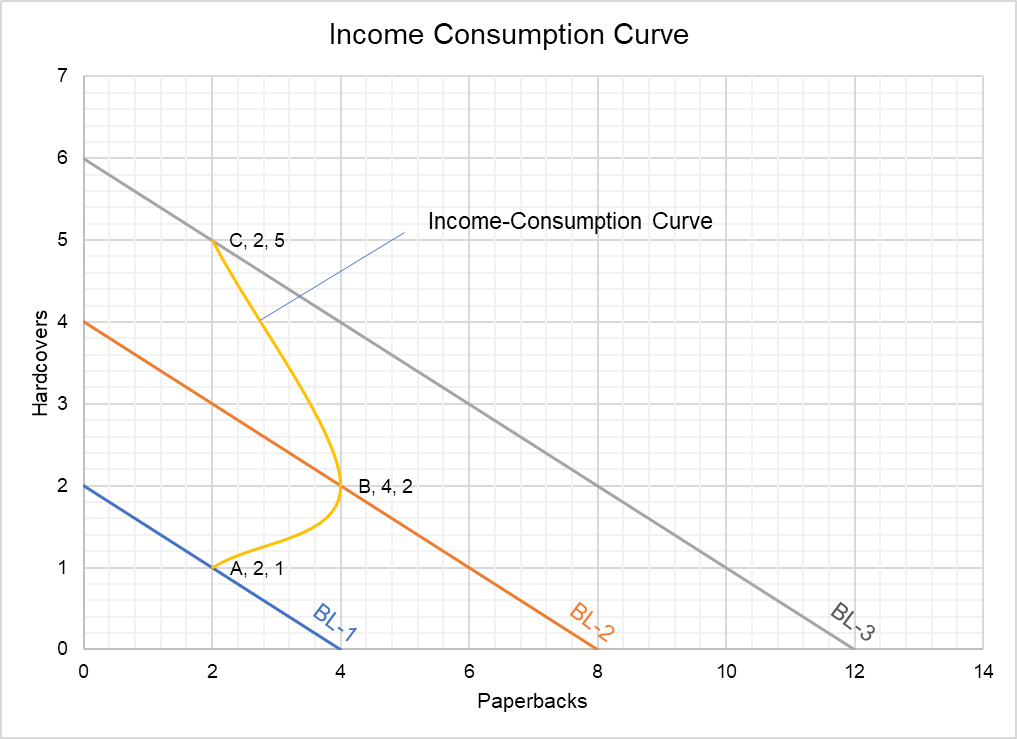
Income consumption curve according to indifference curve theory. The aim of the consumer is to get maximum satisfaction from his money income. It may however be pointed out that given an indifference map and a set of budget lines there will be one income consumption curve. 8 23 income consumption curve icc slopes downward to the right beyond point q 2 i e bends towards the x axis. The term consumer s equilibrium refers to the amount of goods and services which the consumer may buy in the market given his income and given prices of goods in the market.
8 31 and 8 32 various possible shapes which income consumption curve can take are shown bereft of indifference curves and budget lines which yield them. Income consumption curve is a graph of combinations of two goods that maximize a consumer s satisfaction at different income levels. It is plotted by connecting the points at which budget line corresponding to each income level touches the relevant highest indifference curve. Indifference curves can be a straight line at a constant marginal rate of substiruuon.
Consumer s equilibrium through indifference curve analysis. Income is useful for what it can buy. 8 22 income consumption curve icc slope backward upward to the left i e bends toward the y axis. Proponents of ordinal theory argue that it is wrong to base the theory of consumption on the assumption that utility can be measured in absolute terms.
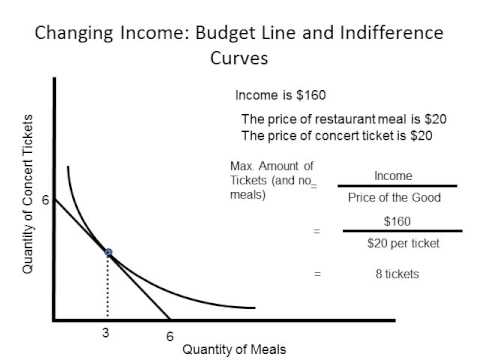
Rational consumers according to this theory a consumer always behaves in a rational manner i e. As indifference curve theory is based on the concept of diminishing marginal rate of substitution an indifference curve is convex to the origin. It therefore seems natural to say that a change in money income and prices that leaves me on the same indifference curve as before has left my real income unchanged. Consumer theory indifference curve analysis ordinal approach according to ordinal theorist a consumer simply ranks or orders his preferences.
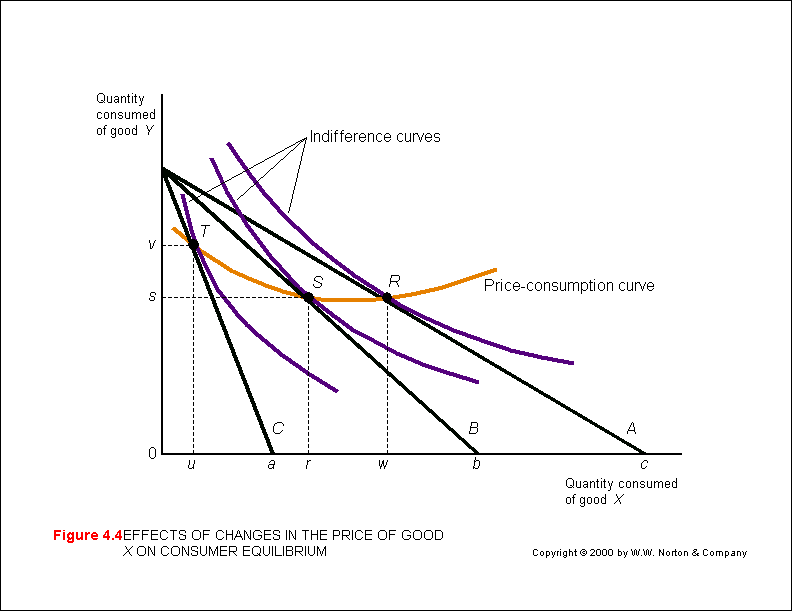
The ratio of exchange between two goods on an indifference curve analysis is shown by the a constant marginal rate of substitution b indifference curve c increasing return to scale d income consumption curve answer. This shows good x to be an inferior good since beyond point q z income effect is negative for good x and as a result its quantity demanded falls as income increases in fig. The price consumption curve pcc is a vertical straight line.